Processes¶
PITLAKQ accounts for the important processes in pit lakes. The figure shows the processes that are explained in the table below.
Please click on the picture to enlarge.
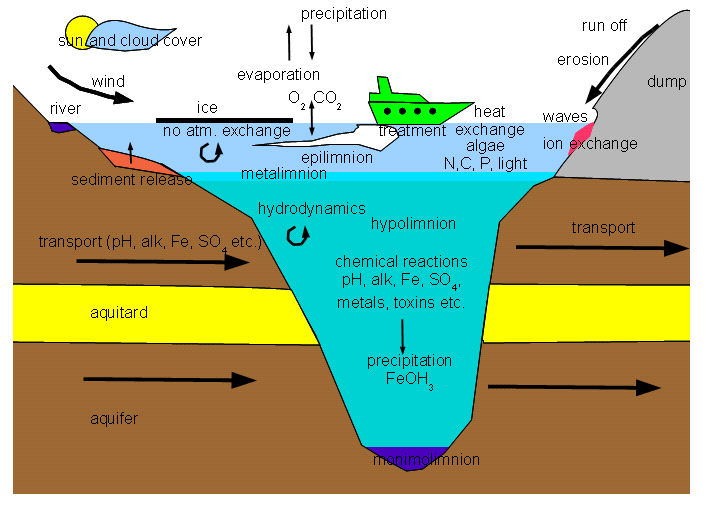
Process |
Description |
Implementation |
|---|---|---|
hydrodynamics |
Solution of the Navier-Stokes-Equation in two dimensions with density-dependent flow. Calculations of velocities, water temperature distribution and hence stratification. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
transport |
Transport of dissolved substance in the lake. Added about 20 species. |
CE-QUAL-W2, PITLAKQ |
heat exchange |
Budgeting of heat terms at water surface. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
wind impact |
Wind energy effects water velocity of upper most lake layer. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
ice cover |
Formation and melting of ice layer. Prevents atmospheric exchange during ice-covered periods. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
tributary inflow |
Inflow from an unlimited number of sources (flow, concentrations, and temperature). |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
atmospheric exchange (O2) |
Oxygen can enter and leave at water surface layer. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
atmospheric exchange (CO2) |
Carbon dioxide can enter and leave at water surface layer. Solubility depends on temperature and pH. |
PITLAKQ |
precipitation |
Precipitation enters surface layer with amount, temperature and concentrations. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
evaporation |
Water evaporates from surface layer. |
CE-QUAL-W2 |
groundwater exchange |
Groundwater characterized by flow, temperature and concentrations can enter and leave lake at any given cell. |
PITLAKQ |
groundwater flow and transport |
The groundwater inflows and outflows can be given as inputs (off-line coupling) or can be supplied by a coupled groundwater model (on-line coupling) to model feedback. |
Groundwater model, PITLAKQ |
erosion (mass input) |
Precipitation and wind waves move material into the lake. |
PITLAKQ |
erosion (water quality impact) |
Eroded material effects lake water quality by adding dissolved substances and cation exchanger loadings that release substances. |
PHREEQC, PITLAKQ |
algae and nutrients |
Algae grow depending on temperature, available light and nutrients. C has been added as limiting nutrient. |
CE-QUAL-W2, PITLAKQ |
chemical lake reactions |
Equilibrium and kinetic reactions in all model cells. Organic matter from biological process is used as electron donators (linking chemical and biological reactions). |
PHREEQC, PITLAKQ |
mineral precipitation |
Forming minerals can be allowed to precipitate. |
PHREEQC, PITLAKQ |
sediment release |
Sediment at lake bottom can release substances. Release rates can be given as function of time or can depend on current lake water composition. |
PITLAKQ |
treatment |
Substances can be added to the lake at any defined location with a time-variable scheme. |
PITLAKQ |
alkalinity of sinks and sources |
In a post-processing step the alkalinity contributions of sinks and sources can be determined with a monthly time step. |
PITLAKQ |
coupling of all processes |
All processes can use information generated by other processes. For example, lake water temperature is used in chemical reactions. |
PITLAKQ |
process additions / modifications |
The model implementation is modular and allows for addition or modification of processes according to site specific needs. |
PITLAKQ |
Please contact us for more information.